What Is The Sequence Of Colors In A Rainbow: A Comprehensive Guide
Rainbows are one of nature's most breathtaking phenomena, and understanding the sequence of colors in a rainbow can deepen our appreciation for this natural wonder. The sequence of colors in a rainbow follows a specific pattern that has fascinated scientists and enthusiasts alike for centuries. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about the sequence of colors in a rainbow, from its scientific explanation to its cultural significance.
A rainbow is not just a beautiful sight; it is also a scientific marvel. When sunlight passes through water droplets in the atmosphere, it refracts, reflects, and disperses, creating the stunning spectrum of colors we see. The sequence of colors in a rainbow is always consistent, and understanding why this happens can enhance our knowledge of optics and meteorology.
This article will take you on a journey through the science behind rainbows, the cultural importance of rainbows, and practical tips for observing them. Whether you're a science enthusiast, a nature lover, or simply curious about the world around you, this guide will provide valuable insights into the sequence of colors in a rainbow.
Read also:Bureau Of Motor Vehicles Portsmouth Ohio Your Complete Guide
Table of Contents
- The Science Behind Rainbows
- Understanding the Sequence of Colors in a Rainbow
- How a Rainbow Forms
- Cultural Significance of Rainbows
- Types of Rainbows
- Double Rainbows: A Special Occurrence
- Tips for Observing Rainbows
- Myths and Legends About Rainbows
- Scientific Facts About Rainbows
- Conclusion
The Science Behind Rainbows
Refraction, Reflection, and Dispersion
Rainbows occur when sunlight interacts with water droplets in the atmosphere. The process involves three key phenomena: refraction, reflection, and dispersion. Refraction occurs when light bends as it enters a water droplet, while reflection happens when the light bounces off the inner surface of the droplet. Dispersion separates the white light into its constituent colors, creating the spectrum we see.
Why Do We See Colors?
White light, such as sunlight, is composed of multiple wavelengths, each corresponding to a different color. When light passes through a water droplet, the different wavelengths bend at slightly different angles, causing the colors to spread out. This dispersion creates the sequence of colors in a rainbow.
Understanding the Sequence of Colors in a Rainbow
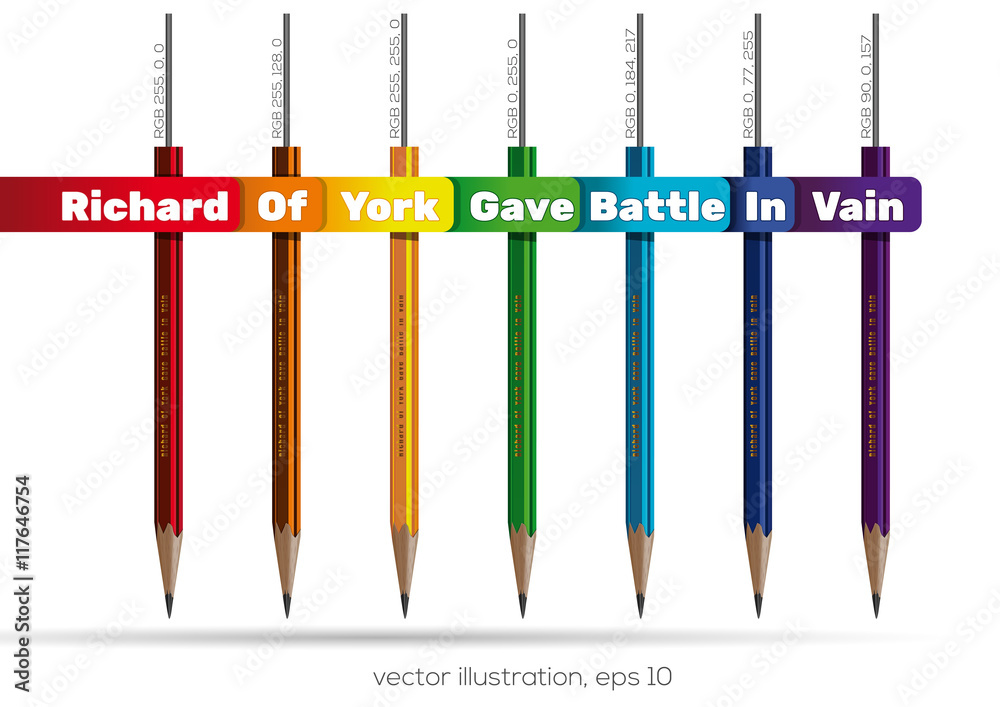
The sequence of colors in a rainbow is always the same: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. This sequence is often remembered using the acronym ROYGBIV. Each color corresponds to a specific wavelength of light, with red having the longest wavelength and violet having the shortest.
Why Does the Sequence Stay the Same?
The consistent sequence of colors in a rainbow is due to the physical properties of light. Longer wavelengths, like red, bend less than shorter wavelengths, like violet. This means that red always appears on the outer edge of the rainbow, while violet appears on the inner edge.
How a Rainbow Forms
A rainbow forms when sunlight passes through raindrops at a specific angle. The angle of refraction and reflection determines the position and appearance of the rainbow. For a primary rainbow, the angle is approximately 42 degrees relative to the observer's line of sight.
Conditions for Rainbow Formation
- Presence of sunlight
- Presence of water droplets in the air
- Observer standing with their back to the sun
Cultural Significance of Rainbows
Rainbows have played a significant role in various cultures throughout history. In many traditions, rainbows symbolize hope, peace, and connection between the earthly and divine realms. For example, in Norse mythology, the rainbow bridge Bifrost connects Earth to Asgard.
Read also:Kylian Mbappeacute Celebration The Art Of Joy On The Field
Modern Symbolism
In modern times, rainbows are often associated with the LGBTQ+ movement, representing diversity and inclusivity. The rainbow flag, designed by Gilbert Baker in 1978, has become an iconic symbol of pride and acceptance.
Types of Rainbows
While the primary rainbow is the most common, there are several other types of rainbows that occur under specific conditions:
- Secondary Rainbow: A fainter rainbow that appears above the primary rainbow, with its colors reversed.
- Supernumerary Rainbows: Additional bands of color that appear near the primary rainbow.
- Monochrome Rainbows: Rainbows that appear in a single color under low-light conditions.
Double Rainbows: A Special Occurrence
What Causes Double Rainbows?
A double rainbow occurs when light reflects twice inside a water droplet. This creates a secondary rainbow above the primary one, with its colors reversed. Double rainbows are rarer than single rainbows but can be observed under the right conditions.
How to Spot a Double Rainbow
To observe a double rainbow, look for a secondary arc above the primary rainbow. The colors in the secondary rainbow will appear in reverse order, with violet on the outer edge and red on the inner edge.
Tips for Observing Rainbows
Observing a rainbow can be a magical experience. Here are some tips to help you spot and appreciate this natural phenomenon:
- Look for rainbows after a rain shower when the sun is shining.
- Position yourself with your back to the sun for the best view.
- Use a camera or smartphone to capture the rainbow's beauty.
- Be patient and observant; rainbows can appear suddenly and disappear just as quickly.
Myths and Legends About Rainbows
Rainbows have inspired countless myths and legends across cultures. In Irish folklore, leprechauns are said to hide their pots of gold at the end of a rainbow. In Hindu mythology, the god Indra uses the rainbow as a weapon to defeat demons. These stories reflect the awe and wonder that rainbows have evoked throughout history.
Scientific vs. Mythical Explanations
While myths provide imaginative explanations for natural phenomena, science offers a deeper understanding of how rainbows work. By combining scientific knowledge with cultural stories, we can appreciate rainbows from both intellectual and emotional perspectives.
Scientific Facts About Rainbows
Rainbows are not just beautiful; they are also fascinating from a scientific standpoint. Here are some interesting facts about rainbows:
- Rainbows are circular, but we usually only see an arc due to the horizon.
- The colors of a rainbow depend on the size of the water droplets.
- Rainbows can occur with moonlight, creating a "moonbow."
- Each person sees their own unique rainbow based on their position.
Conclusion
The sequence of colors in a rainbow is a testament to the beauty and complexity of nature. From the science of refraction and dispersion to the cultural significance of rainbows, this natural phenomenon continues to inspire and educate people around the world. By understanding the science behind rainbows and appreciating their cultural importance, we can deepen our connection to the natural world.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with rainbows in the comments below. Have you ever seen a double rainbow or a moonbow? What does a rainbow mean to you? Don't forget to explore other articles on our site for more fascinating insights into the wonders of nature.
For further reading, check out these trusted sources:
Article Recommendations